
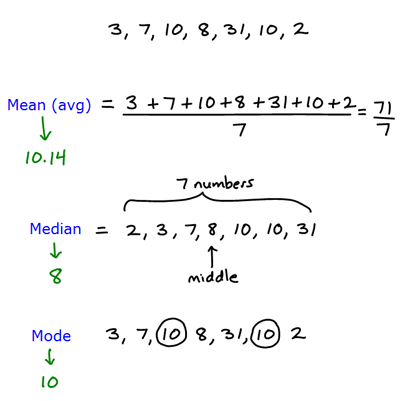
They mean the same thing, but in the context of math and statistics, it’s better to use the word mean to distinguish from other things that might be casually referred to as “average” values in a general sense (meaning values that are the most representative or common within the set). In math, the word mean refers to what’s informally called the average. The mode is simply the value that occurs the most in the set. When you arrange a set of values from smallest to largest, the median is the one in the middle. 10, 5, 25, 50, 15, 10, 40, 35, 10, 20 5, 10, 10, 10, 15, 20, 25, 35, 40, 50 What is the mean? What is the median? What is the mode? What is the range? Answers: Mean: 10 Median: 17.You find the mean (informally called the average) by adding up all the numbers in a set and then dividing by how many values there are. 35, 40, 45, 50 50 - 15 = 40 40 is the range of this set of numbers Subtract the lowest number from the highest number in a set of numbers Example: 10, 15, 20, 25, 30. The difference between the highest and lowest numbers in a set of numbers (Note: Putting the numbers in numerical order will help) įind the range. (Note: Putting the numbers in order will help to identify the mode) The number in a set of numbers that occurs the most often. Example 1 10, 15, 20 The median of the set of numbers is 15 Example 2 10, 15, 20, 25 Add 15 + 20 = 35 Divide 35 by 2 = 17.5 The median of the set of numbers is 17.5 Is the number that is in the middle of a set of numbers (Note: The numbers must be in numerical order) If two numbers make up the middle of a set of numbers then the median is the average of these two numbers įind the median.

Add all the numbers in the set together Divide the sum by the number of numbers in the set The quotient is the mean of the set of numbers Example: 20, 15, 25 Add 20 + 15 + 25 = 60 Divide 60 by 3 The mean is 20


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
